Natural gas explained
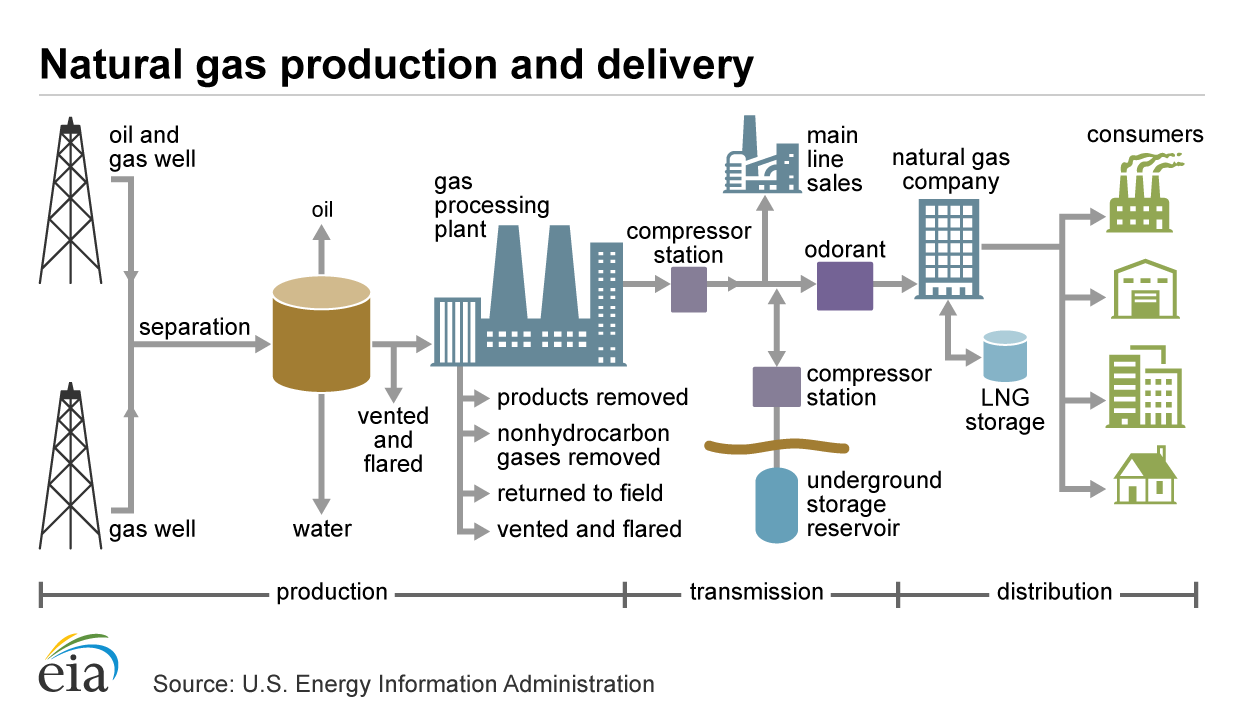
Use of natural gas
The United States used about 30.5 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of natural gas in 2020, the equivalent of about 31.5 quadrillion British thermal units (Btu) and 34% of U.S. total energy consumption.
Natural gas use by U.S. consuming sectors by amount and percentage share of total U.S. natural gas consumption in 2020 was:1
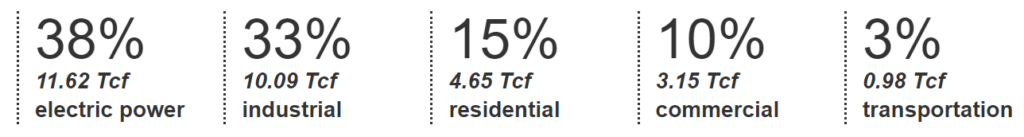
How natural gas is used in the United States
Most U.S. natural gas use is for heating and generating electricity, but some consuming sectors have other uses for natural gas.
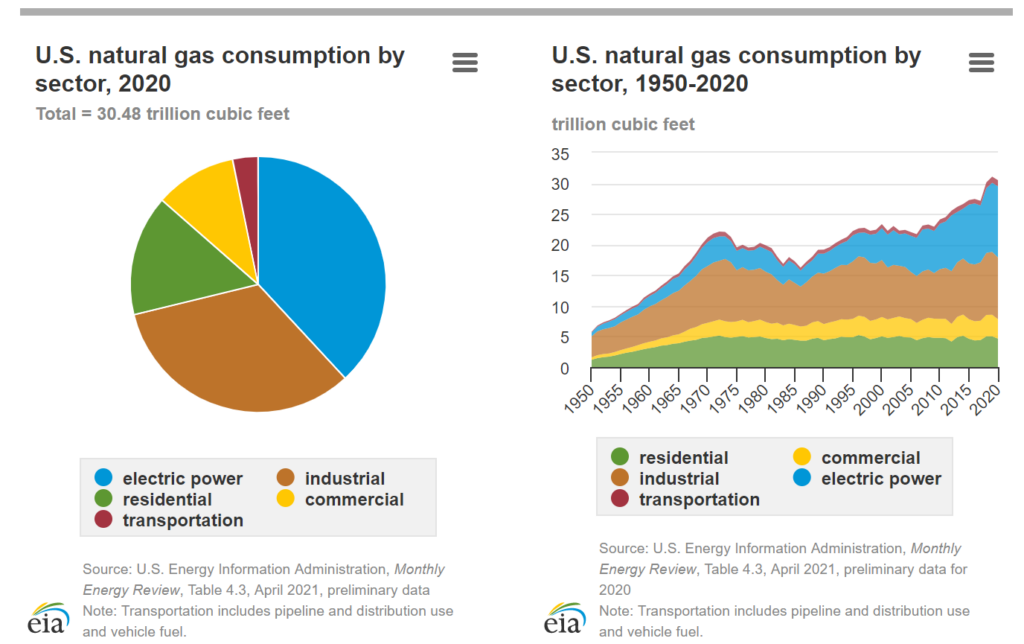
The electric power sector uses natural gas to generate electricity and produce useful thermal output. In 2020, the electric power sector accounted for about 38% of total U.S. natural gas consumption, and natural gas was the source of about 33% of the U.S. electric power sector’s primary energy consumption. Most of the electricity produced by the electric power sector is sold to and used by the other U.S. consuming sectors, and that electricity use is included in each sector’s total energy consumption. (The industrial and commercial sectors also use natural gas to generate electricity, and they use nearly all of this electricity themselves.) Natural gas accounted for 40% of total utility-scale U.S. electricity generation by all sectors in 2020.
The industrial sector uses natural gas as a fuel for process heating, in combined heat and power systems, as a raw material (feedstock) to produce chemicals, fertilizer, and hydrogen, and as lease and plant fuel. In 2020, the industrial sector accounted for about 33% of total U.S. natural gas consumption, and natural gas was the source of about 34% of the U.S. industrial sector’s total energy consumption.2
The residential sector uses natural gas to heat buildings and water, to cook, and to dry clothes. About half of the homes in the United States use natural gas for space heating and water heating. In 2020, the residential sector accounted for about 15% of total U.S. natural gas consumption, and natural gas was the source of about 23% of the U.S. residential sector’s total energy consumption.
The commercial sector uses natural gas to heat buildings and water, to operate refrigeration and cooling equipment, to cook, to dry clothes, and to provide outdoor lighting. Some consumers in the commercial sector also use natural gas as a fuel in combined heat and power systems. In 2020, the commercial sector accounted for about 10% of total U.S. natural gas consumption, and natural gas was the source of about 19% of the U.S. commercial sector’s total energy consumption.
The transportation sector uses natural gas as a fuel to operate compressors that move natural gas through pipelines and as a vehicle fuel in the form of compressed natural gas and liquefied natural gas. Nearly all vehicles that use natural gas as a fuel are in government and private vehicle fleets. In 2020, the transportation sector accounted for about 3% of total U.S. natural gas consumption. Natural gas was the source of about 4% of the U.S. transportation sector’s total energy consumption in 2020, of which 94% was for natural gas pipeline and distribution operations.
Where natural gas is used
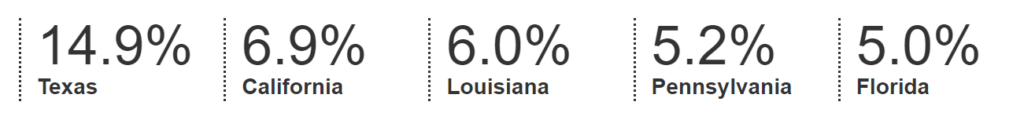
Natural gas is used throughout the United States, but five states accounted for about 38% of total U.S. natural gas consumption in 2019.
The five largest natural gas-consuming states and their percentage shares of total U.S. natural gas consumption in 2019 were:3
1 Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Monthly Energy Review, Table 4.3, April 2021, preliminary data. Sum of shares may not equal 100% because of independent rounding.
2 Total energy consumption is primary energy consumption in the end‐use sectors, plus electricity retail sales to the sectors and electrical system energy losses. Also includes other energy losses throughout the energy system.
3 Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Natural Gas Annual, September 2020
Last updated: May 26, 2021







